What’s new in ETE 2.2¶
BUGFIXES¶
- Fixes in NeXML parser and exporting functions
- Fixed ‘paste newick’ functionality on the GUI
- Fixed
PhyloNode.is_monophyletic()and moved toTreeNode.check_monophyly(). - Fixed consistency issued in
TreeNode.sort_descendants()function.
SCRIPTS¶
- Improvements in the standalone visualization script (a.k.a. ete2)
- Added the etree2orthoxml script, which provides conversion between phylogenetic tree and the orthoXML format
NEW MODULES¶
New
EvolNodetree object type is available as a part of adaptation-test extension recently developed by François Serra (see Testing Evolutionary Hypothesis in the tutorial).
NEW FEATURES¶
News in core Tree instances:
Added
TreeNode.robinson_foulds()distance to compare the topology of two trees (i.e. tree.robinson_foulds(tree2)). It includes automatic pruning to compare trees of different sizes. See tutorial and examplesAdded new options to
TreeNode.copy()function, allowing faster methods to duplicate tree node instances. See tutorial and examplesAdded
preserve_branch_lengthargument toTreeNode.prune()andTreeNode.delete(), which allows to remove nodes from a tree while keeping original branch length distances among the remaining nodes.Added
TreeNode.resolve_polytomy()function to convert multifurcated nodes into an arbitrary structure of binary split nodes with distance. See tutorial and examplesAdded
TreeNode.get_cached_content()function, which returns a dictionary linking each node instance with its leaf content. Such a dictionary might be used as a cache to speed up functions that require intensive use of node traversing. See tutorial and examplesImproved
TreeNode.get_ascii()function for text-based visualization of trees. A new attributes argument can be passed to display node attributes within the ASCII tree representation.from ete2 import Tree t = Tree("((A, B)Internal_1:0.7, (C, D)Internal_2:0.5)root:1.3;", format=1) t.add_features(size=4) print t.get_ascii(attributes=["name", "dist", "size"]) # # /-A, 0.0 # /Internal_1, 0.7 # | \-B, 0.0 # -root, 1.3, 4 # | /-C, 0.0 # \Internal_2, 0.5 # \-D, 0.0 #
Random branch length and support values generation is now available for the
TreeNode.populate()function.a new argument
is_leaf_fnis available for a number of traversing functions, thus allowing to provide custom stopping criteria when browsing a tree. This is, any node matching the function provided through theis_leaf_fnargument will be temporarily considered as a terminal/leaf node by the traversing function (tree will look as a pruned version of itself). See tutorial and examplesAdded
TreeNode.iter_ancestors()andTreeNode.get_ancestors()functions.Added
TreeNode.iter_prepostorder()tree node iterator.Newick parser accepts now the creation of single node trees. For example, a text string such as
"node1;"will be parsed as a single tree node whose name isnode1. By contrast, the newick string(node1);will be interpreted as an unnamed root node plus a single child namedname1.TreeNode.write()accepts now aformat_root_nodeargument to export root node features as a part of the newick string.The new
TreeNode.check_monophyly()method allows to check if a node is mono, poly or paraphyletic for a given attribute and values (i.e. grouped species). Although monophyly is actually a phylogenetic concept, the idea can be applied to any tree, so any topology could be queried for the monophyly of certain attribute values. If not monophyletic, the method will return also the type of relationship connecting the provided values (para- or poly-phyletic). See tutorial and examplesNew
TreeNode.get_monophyletic()method that returns a list of nodes in a tree matching a custom monophyly criteria.
News PhyloTree instances:
Added
PhyloNode.get_speciation_trees()method, which returns all possible species topologies present in a gene family tree as described in Treeko. See tutorial and examplesSee also
TreeKO: a duplication-aware algorithm for the comparison of phylogenetic trees.
Marcet-Houben M, Gabaldón T.
Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 May;39(10):e66. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr087.
Added
PhyloNode.split_by_dups()method, which returns a list of partial subtrees resulting from splitting a tree at duplication nodes. See tutorial and examplesAdded
PhyloNode.collapse_lineage_specific_expansions()method, which returns a pruned version of a tree, where nodes representing lineage specific expansions are converted into a single leaf node. See tutorial and examples
News on sequence and multiple sequence alignment parsing:
- added the option to disable the automatic correction of duplicated
names when loading
SeqGroupdata from phylip and fasta files.
- added the option to disable the automatic correction of duplicated
names when loading
News on tree visualization and image rendering:
node style attributes can now be modified without the need of initialization by directly accessing the
TreeNode.img_styleattribute.Multiple layout functions can now be provided to combine their functionality. This way, you can keep separate styling templates and combine them as necessary.
from ete2 import TreeStyle def color_leaves(node): if node.is_leaf(): node.img_style["fgcolor"] = "red" def size_internal(node): if not node.is_leaf(): node.img_style["size"] = 15 ts = TreeStyle() # provide a list of layout functions, instead of a single one ts.layout_fn = [color_leaves, size_internal]
COLOR_SCHEMESandSVG_COLORSdictionaries are provided for easy access to color codes and several predefined color schemes. In addition, arandom_color()function is also available as a generator of RGB colors (where saturation and lightness can be fixed).from ete2 import random_color, COLOR_SCHEMES, SVG_COLORS # generate 20 random colors node_colors = [random_color(s=0.4, l=4) for i in xrange(20)]
News on node faces:
New
face.rotationattribute, that allows to rotate individual faces even when a globaltreestyle.rotationis used.Improved
SequenceFace: Sequence sites are now rendered one by one, allowing interaction with each of them and getting rid of the previous pixmap size limitation. Site image dimensions and colours are now configurable.Added new
SeqMotifFaceclass, which represent an enriched version of the formerSequenceFaceinstance. This new face type allows to represent sequences as a succession of domain/motif elements or to represent sequence positions as color points. Gaps can also be taken into account and therefore shown as as a black space or a flat line.Added
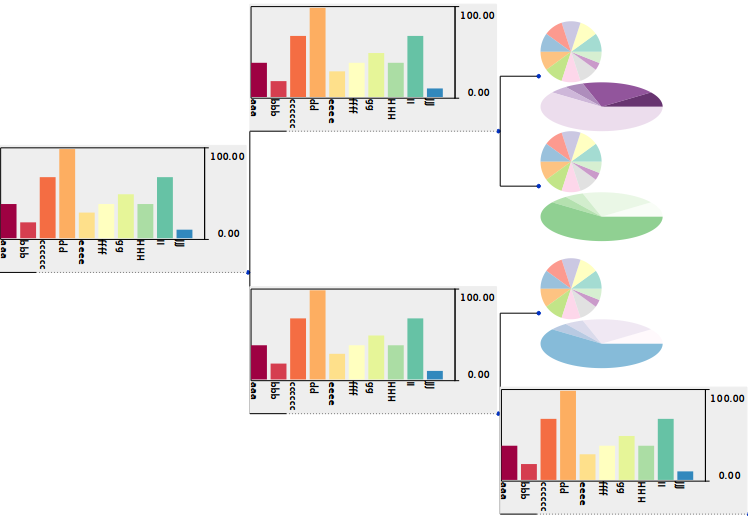
PieChartFaceandBarChartFaceface types for built-in representation of statistics attached to nodes.Improved
ImgFaceclass, now accepting on the fly image scaling.
News on the GUI
- Allows image region selection.
- Allows zooming on selected regions or specific nodes (Z - zoomIn, X - zoomOut, R - focus region).
C-cwill now interrupt the GUI application when started from a terminal.- Added keyboard-based node navigation (click on a node and play the arrow keys).